Definition of an Externality in Environmental Economics:
Externality emerges when one person's consumption and production decision affects another entity without that entities permission or compensation.
Types of externality:
(1) Positive externality: Positive externality emerges when one person's or groups action have favorable impact on another party. For example- If a Gardener invests in the beautification of his garden, it will not only enhance his property value but also enhances the property value of neighboring houses.
Again, positive externality classification on the basis of sources:
(i) Positive production externality: Positive production externality emerges when one person's production decision have some favorable impact on another person. For example- If a person invests to build a factory in an area, the nearby people will be benefited through getting good infrastructural facilities such as- electricity, road ways etc.
(ii) Negative production externality: Negative production externality emerges when one person's or groups production decision have some unfavorable impact on another person's or groups. For example- If a factory dumps the waste generated in his production activity in the nearby river, it may adversely effect on another person's who use the river water for his for their own purpose.
(iii) Positive consumption externality: Positive consumption externality emerges when one person's or groups consumption decision have some favorable impact on another party. For example- Wearing of mask by individual will not only reduce his chances of getting infected but also decreases the likelihood of other being infected through the contract with the individual.
(iv) Negative consumption externality: Negative consumption externality emerges when one person's or groups have some unfavorable consumption decision impact on another person's or groups or party. For example- The consumption of cigarette by individual in an open space may create disutility to the non-smokers.
(2) Negative externality: Negative externality emerges when one person's or groups action have some unfavorable impact on another party. For example- If a factory dumps the waste generated in his production activity in the nearby river, it may adversely effect other people who use the river water for their own purpose.
Externality is the reason behind market failure:
Externality emerges when one person's consumption and production decision affects another entity without that entities permission or compensation. Externality can be broadly classified into two categories- positive externality and negative externality.
However, whatever be it's type, in the presence of externality there exists divergence between Marginal social benefit (MSB) and Marginal social cost (MSC). Thus it appears that in the presence of externality Pareto's optimality can not be ensure. This is because Pareto's optimality is ensure only when marginal social benefit (MSB) become equal to marginal social cost (MSC).
Now, let us take the case of negative externality-
Negative externality emerges when one person's or groups action have some unfavorable impact on another party. Now let us take the case of a paper production factory. The production process involved uses of various types of resources such as raw materials, labours, machining, etc. The firm while calculating it's cost of production will only include the monetary payment mode, this imposed and accordingly said the supply function of paper.
However, in the process of paper production some amount of wastes or garbage generating and the firm dumps this garbage into a nearby river. This again cost serious health damage to the people who use the river water for them own purpose.
Thus the process of paper production actually imposed some amount of external cost on the society but this external cost will not be included by the firm it's supply function hence Marginal social cost (MSC) will be greater than marginal private cost (MPC).
Accordingly price of the commodity will set as a lower level then society optimum or Pareto's optimum level. Thus it can be concluded that in the presence of negative externality market mechanism fails to operate efficiently that is market failure occur.
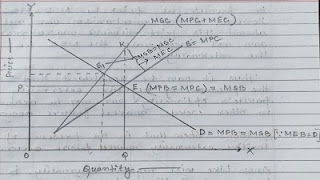
Assumption: There is no marginal externality benefit (MEB=0).
NOTE: { (MSB=MPB+MEB) (MSC=MPC+MEC) }
In the above diagram the demand curve actually represent the MPB (Marginal private benefit) curve. Since Marginal external benefit (MEB) has been assumed to be zero. Therefore MPB=MSB. Again S is the supply curve. Which also represent marginal private cost (MPC) curve. Since, the process of paper production imposes some amount of external cost to the society hence the Marginal social (MSC) curve has been drawn above the MPC curve.
The difference between MSC and MPC actually represent the MEC (KE). Accordingly price of paper is determined at OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ. However, this not Pareto's optimum level because MSB and MSC are not equal.
In the diagram it can seen that Pareto's optimum or market success can be achieved at point E¹, MSB=MSC. However, market mechanism can not attend this point because market process can not incorporate the MEC that is the externality.
Thus it can be concluded that in the presence of negative externality Pareto's optimality can not be achieve in other words market failure occur.







0 Comments
Please do not Enter any Spam link in the Comment box.