Hi Friends Welcome to my Website 'theeconomicsstudy.in' and also thank you very much for come to my website. In today's article we are going to know 'Define Offer Curves?. So let's discuss this.
Define Offer Curves?
The concept of offer curve or Reciprocal demand curve originally given by Marshall and Edgeworth. The trade offer curve or reciprocal demand curve indicates what quantities of a particular commodity that one country is willing to offer in exchange of certain quantities of another commodity.Offer Curve derivation
J.S. Mill's approach to gains from trade in terms of trade offer curve
The
distribution of gains from trade was provided by J.S. Mill. He attempted to
analysis both the gains from trade and their distribution among the trading
countries. He emphasised upon the concept of reciprocal demand that determines the
terms of trade which is a ratio of quantity imported to the quantity exported
by the given country.
The distribution of gains from trade can be explained with the help of offer curves-
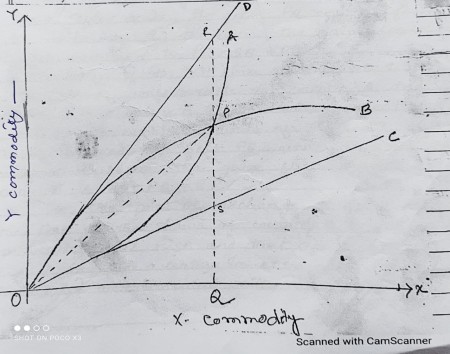
In the above figure on OX axis we measure X commodity which exported by country A and OY axis we measure Y commodity which is exported by country B. In the figure, OA and OB are the offer curves of countries A and B respectively. Here, OC and OD are the domestic exchange ratio lines for countries A and B respectively.In the
figure, P is the point of exchange where OA and OB are cut each other.
TOT (Terms of trade) for at P=QM/QX
=PQ/OQ
= Slope of line OP.
If the line
OP gets closer to OD, the terms of trade becomes favourable to country A and
unfavourable to country B. Here, before trade country A was willing to exchange
SQ units of Y for OQ units of X. After trade, it gets or willing to to exchange
PQ units of Y for OQ units of X. Therefore, the gain from trade for country A
is PQ-SQ=PS.
Similarly,
if the OP line gets closer to OC, the TOT becomes unfavourable to country A and
unfavourable to country B. Before trade, country B was willing to export RQ
units of Y for OQ units of X. After trade, it gets PQ units of Y for OQ units
of Y. Therefore, the gain from trade for country B is RQ-PQ=RP.
Here, As the point of exchange P gets closer to the line OD, the share of country A in the gain from trade will rise and that of country B will fall and vice-versa. In this way, the gain is distribution on measured with the help of offer curves.
Conclusion
So friends, this was 'Define Offer Curves?'. Hope you get the full details about it and hope you like this article.
If you like this article, share it with your friends and turn on the website Bell icon, so don't miss any articles in the near future. Because we are bringing you such helpful articles every day. If you have any doubt about this article, you can comment us. Thank You!







0 Comments
Please do not Enter any Spam link in the Comment box.