Business Cycle in economics
Business cycle (trade cycle) is a part of the capitalist system which refers to the phenomenon of cyclical booms and depressions. In a business cycle there are wake like fluctuations in aggregate employment income output and price level. In other words, trade cycle refers to the rhythmic flustuations in economic activities specially in employment, output and income, prices, profits etc.
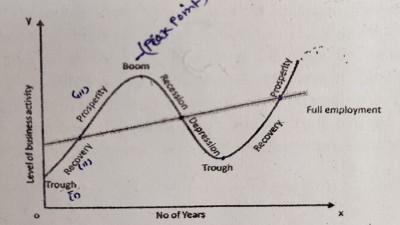
Usually a Business Cycle (or Trade Cycle) is divided into four phases which are discussed by the following diagram-(Business cycle graph)
4 Phases of Business cycle
The business cycle starts from a lower point and passes through a recovery phase followed by a period of expansion or upper turning point and prosperity. After the peak point is reached then there is a declining phase of recession followed by a depression and again the business cycle continuous (similarly with) with ups and downs. The four phases of a business cycle are briefly explained as follows point-
(i) Depression Phase: Under the depression slump phase both economic activities and national income fall and the cost is comparatively higher than price. Level of profit decreases and there is a reduction in the consumer and also capital goods. The bank credits goes decline. In simple word during the period of depression the level income, employment, consumption, standard of living, prices comes to the lowest (minimum) level. In depression, there is under utilization of resources and fall in Gross National Product (GNP).
(ii) Recovery Phase: The turning point from the depression to expansion is termed as (called as) Recovery or Revival Phase. During the period or time of revival or recovery, there are expansions and rise in économic activities. When demand starts rising then the production Increases and this causes an Increase in investment. There is a steady rise in output,employment, income, prices and profits.
The businessmen gain confidence and become optimistic (Positive). This increases investment. The simulation of Investment brings about the revival or recovery of the economy. All the banks are expand their credit, the business expansion takes place and stock markets are activated. Revival slowly emerges into the prosperity and the business cycle is repeated again.
(iii) Prosperity Phase: In the Prosperity stage, When there is an expansion of employment, price, output, income, profits and there is rise in the standard of living of people. This period is termed as or called as Prosperity phase or stage. The prosperity phase or stage is the highest level of revival phase of the trade cycle. When there is a raise in profits, businesses are able to get loans from the financial institutions.
As the demand increased for bank credits and loans, the rate of interest reaches the highest floor, which leads to sharp rise in the prices. Due to full employment of the resources and a high level of economic activity, it causes a rise in prices and profits. There is an upswing in the economic activity and the economy when it reaches the Peak point. This situation is also called as Boom Period.
(iv) Recession Phase: The turning point from the prosperity to depression is called as Recession (termed as) Phase or stage. During the period of recession, the economic activities slow down. When the demand starts falling that situation the overproduction and future investment plans are also given up. There is a steady decline in the employment, output, price, profits and the businessmen lose confidence and become pessimistic.
It reduces the investment level and the banks and the people try to get greater liquidity, so the credit also contracts. Expansion of business stops, stock market falls and all the Orders are cancelled and people start losing their jobs. The increase in unemployment causes a sharp dedine in income and aggregate demand. Generally, recession lasts for a short period.







0 Comments
Please do not Enter any Spam link in the Comment box.