The pollution and degradation of environmental quality can be controlled with the help of two methods.
(i) Command and Control approach
(ii) Incentive based approach
Command and Control approach
Command and Control approach is the popular form of environmental
regulation in the world today. It can be defined as the direct regulation of an
activity by legislation that states what is permitted and what is illegal. The
Command is presentation of quality standards by the govt authority that must be
maintained. The regulator collects the information and he decides his action.
Merits of Command and Control Approach
(i) It has been proposed by imposing fixed standards
with the force of law, this approach can respond more quickly.
(ii) This approach improves the behavior of the
regulator and quality of the environment.
Demerits of Command and Control approach
(i) This method is very costly because the cost of
information and command is very high.
(ii) The polluters pay only for pollution control not
residual damage from the pollution that still emitted even after controls are
in place.
(iii) This approach is not applicable in the UDCs
(Under develop Countries) where most of the people are illiterate.
Incentive based approach or Market based approach
Economic incentives provide rewards for polluters to do
what is perceived to be in the public interest in the context of pollution,
there are three basic types of incentives.
(i) Marketable or tradable permit: A marketable permit
allows polluters to buy and sell the rights to pollute here pollution becomes a
very expensive activity. This is because less pollution means fewer permits need
be bought.
(ii) Liability: Liability is another type of intensive. Under this
system, when someone under takes a risky activity (Such as air pollution) that
person will take all potential damage from his activity into account when he
performs the activity. The important issue is that the govt is not telling what
to do, just aware that the polluters will be responsible for any consequences.
This creates an incentive to be careful when under taking risky activity. It is
an important method of controlling pollution.
(iii) Pollution Tax: Pollution fees or tax involve the
payment of a charge per unit of population emitted. Higher pollution denotes
higher pollution tax. It is an important method of pollution control.
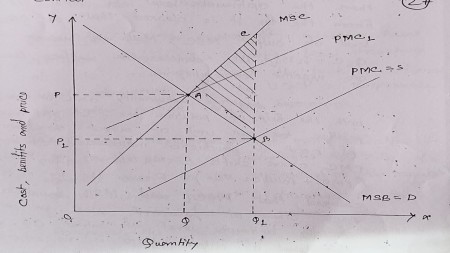
The negative externality can be remove with the help
of pollution tax. If govt impose pollution tax per unit of output then marginal
cost of production increases. As a result PMC curve shifts to the left to PMC1
(PMC+Pollution tax). From the figure it is cleared that PMC1 and MSB equal to
each other at point A where we get socially optimum level of output OQ. At this
level of output there is no external effects. In this case can remove negative
externality.
Merits of incentive based approach
(i) The economic incentive based methods provide
revenue to the govt.
(ii) These methods control the damage of the
environment very quickly than the command and control methods.
Demerits of incentive based approach
(i) The success of incentive based approach requires a
strong legal structure of the country. But the lack of efficient legal
structure of the UDC is responsible for slow action of this approach.
(ii) Economic incentives will be more effective if
competition plays a meaningful role in the economy and in the decisions of the
regulators. But the market structure of the UDC is imperfect in nature which
hampers the action of these methods.
(iii) The effectiveness of economic incentive based method requires political stability and political wills.







0 Comments
Please do not Enter any Spam link in the Comment box.